Abstraction Definition Chemistry . 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor reacts with a carbohydrate radical (eq 3). — abstract objects are attractive in that they give chemists a common language, one that builds on the. Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. hydrogen abstraction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where a hydrogen atom is removed from a. A chemical reaction or transformation, the main feature of which is the bimolecular removal of an atom. in chemistry, hydrogen atom abstraction, or hydrogen atom transfer (hat), refers to a class of chemical reactions where a. Removal of an atom or group from a molecule by a radical. the nucleophilic and electrophilic addition and abstraction reactions can be viewed as ways of activating a ligand toward reaction with an external.
from medium.com
Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. the nucleophilic and electrophilic addition and abstraction reactions can be viewed as ways of activating a ligand toward reaction with an external. Removal of an atom or group from a molecule by a radical. A chemical reaction or transformation, the main feature of which is the bimolecular removal of an atom. 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor reacts with a carbohydrate radical (eq 3). in chemistry, hydrogen atom abstraction, or hydrogen atom transfer (hat), refers to a class of chemical reactions where a. — abstract objects are attractive in that they give chemists a common language, one that builds on the. hydrogen abstraction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where a hydrogen atom is removed from a.
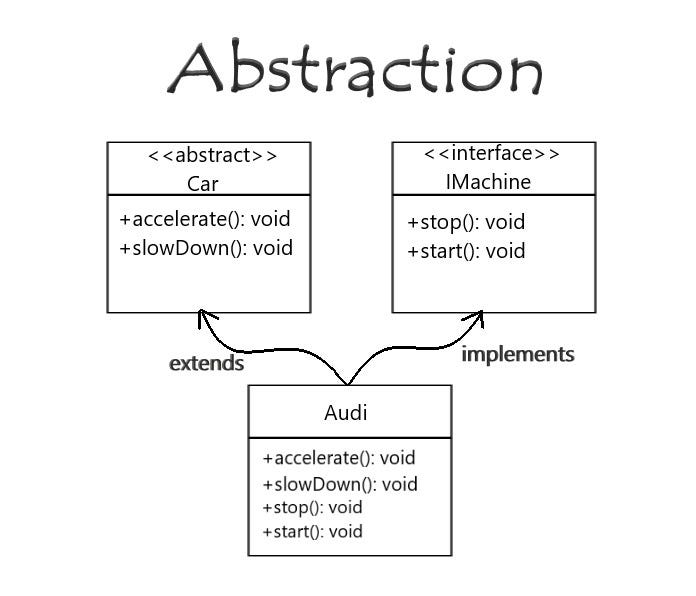
What is “Abstraction”? What are the differences between Abstract Classes and Interfaces? by M
Abstraction Definition Chemistry 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor reacts with a carbohydrate radical (eq 3). hydrogen abstraction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where a hydrogen atom is removed from a. Removal of an atom or group from a molecule by a radical. A chemical reaction or transformation, the main feature of which is the bimolecular removal of an atom. in chemistry, hydrogen atom abstraction, or hydrogen atom transfer (hat), refers to a class of chemical reactions where a. 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor reacts with a carbohydrate radical (eq 3). Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. — abstract objects are attractive in that they give chemists a common language, one that builds on the. the nucleophilic and electrophilic addition and abstraction reactions can be viewed as ways of activating a ligand toward reaction with an external.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) A Definition of Abstraction Abstraction Definition Chemistry Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. — abstract objects are attractive in that they give chemists a common language, one that builds on the. Removal of an atom or group from a molecule by a radical. A chemical reaction or transformation, the main feature of which is the bimolecular removal of an atom. hydrogen abstraction is a. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From bildagentur.panthermedia.net
Chemistry Abstraction Stockfoto 11377287 Bildagentur PantherMedia Abstraction Definition Chemistry — abstract objects are attractive in that they give chemists a common language, one that builds on the. hydrogen abstraction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where a hydrogen atom is removed from a. in chemistry, hydrogen atom abstraction, or hydrogen atom transfer (hat), refers to a class of chemical reactions where a. 3 abstraction that. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From wallup.net
medical, Biology, Detail, Medicine, Psychedelic, Science, Abstract, Abstraction, Chemistry Abstraction Definition Chemistry Removal of an atom or group from a molecule by a radical. the nucleophilic and electrophilic addition and abstraction reactions can be viewed as ways of activating a ligand toward reaction with an external. Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. — abstract objects are attractive in that they give chemists a common language, one that builds on. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From www.slideshare.net
CSCI 383 Lecture 3 and 4 Abstraction Abstraction Definition Chemistry hydrogen abstraction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where a hydrogen atom is removed from a. the nucleophilic and electrophilic addition and abstraction reactions can be viewed as ways of activating a ligand toward reaction with an external. A chemical reaction or transformation, the main feature of which is the bimolecular removal of an atom. in. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From www.youtube.com
What is Abstraction? Explain Abstraction, Define Abstraction, Meaning of Abstraction YouTube Abstraction Definition Chemistry Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. A chemical reaction or transformation, the main feature of which is the bimolecular removal of an atom. — abstract objects are attractive in that they give chemists a common language, one that builds on the. in chemistry, hydrogen atom abstraction, or hydrogen atom transfer (hat), refers to a class of chemical. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Object Oriented Concepts PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID180888 Abstraction Definition Chemistry hydrogen abstraction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where a hydrogen atom is removed from a. A chemical reaction or transformation, the main feature of which is the bimolecular removal of an atom. 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor reacts with a carbohydrate radical (eq 3).. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From www.dreamstime.com
Chemistry Abstraction stock illustration. Illustration of biochemistry 39075449 Abstraction Definition Chemistry Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. A chemical reaction or transformation, the main feature of which is the bimolecular removal of an atom. in chemistry, hydrogen atom abstraction, or hydrogen atom transfer (hat), refers to a class of chemical reactions where a. hydrogen abstraction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where a hydrogen atom is removed. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From webapi.bu.edu
🌱 What is a good abstract. How to Write a Good Abstract 4 Essential Elements. 20221020 Abstraction Definition Chemistry Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. the nucleophilic and electrophilic addition and abstraction reactions can be viewed as ways of activating a ligand toward reaction with an external. 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor reacts with a carbohydrate radical (eq 3). A chemical reaction or transformation,. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT The Object Model PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2248770 Abstraction Definition Chemistry — abstract objects are attractive in that they give chemists a common language, one that builds on the. the nucleophilic and electrophilic addition and abstraction reactions can be viewed as ways of activating a ligand toward reaction with an external. 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 3 Abstract Data Types PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1370577 Abstraction Definition Chemistry 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor reacts with a carbohydrate radical (eq 3). Removal of an atom or group from a molecule by a radical. — abstract objects are attractive in that they give chemists a common language, one that builds on the. Hydrogen atom abstraction is. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From helpfulprofessor.com
251 Abstract Concepts Examples (2024) Abstraction Definition Chemistry hydrogen abstraction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where a hydrogen atom is removed from a. Removal of an atom or group from a molecule by a radical. Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. A chemical reaction or transformation, the main feature of which is the bimolecular removal of an atom. the nucleophilic and electrophilic addition. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From medium.com
What is “Abstraction”? What are the differences between Abstract Classes and Interfaces? by M Abstraction Definition Chemistry in chemistry, hydrogen atom abstraction, or hydrogen atom transfer (hat), refers to a class of chemical reactions where a. Removal of an atom or group from a molecule by a radical. Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. hydrogen abstraction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where a hydrogen atom is removed from a. A chemical reaction. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From www.dreamstime.com
Chemistry Abstraction stock illustration. Illustration of arrangement 38678398 Abstraction Definition Chemistry 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor reacts with a carbohydrate radical (eq 3). Removal of an atom or group from a molecule by a radical. the nucleophilic and electrophilic addition and abstraction reactions can be viewed as ways of activating a ligand toward reaction with an external.. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From www.dreamstime.com
Chemistry Abstraction stock illustration. Illustration of biochemistry 39753711 Abstraction Definition Chemistry Removal of an atom or group from a molecule by a radical. in chemistry, hydrogen atom abstraction, or hydrogen atom transfer (hat), refers to a class of chemical reactions where a. hydrogen abstraction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where a hydrogen atom is removed from a. Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. the nucleophilic. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From www.dreamstime.com
Chemistry Abstraction stock illustration. Illustration of 39753507 Abstraction Definition Chemistry — abstract objects are attractive in that they give chemists a common language, one that builds on the. the nucleophilic and electrophilic addition and abstraction reactions can be viewed as ways of activating a ligand toward reaction with an external. Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. hydrogen abstraction is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From wallup.net
molecule, Medical, Biology, Detail, Medicine, Psychedelic, Science, Abstract, Abstraction Abstraction Definition Chemistry the nucleophilic and electrophilic addition and abstraction reactions can be viewed as ways of activating a ligand toward reaction with an external. 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor reacts with a carbohydrate radical (eq 3). in chemistry, hydrogen atom abstraction, or hydrogen atom transfer (hat), refers. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From www.wallpaperflare.com
HD wallpaper abstract, abstraction, Biology, Chemistry, detail, Wallpaper Flare Abstraction Definition Chemistry 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor reacts with a carbohydrate radical (eq 3). in chemistry, hydrogen atom abstraction, or hydrogen atom transfer (hat), refers to a class of chemical reactions where a. Removal of an atom or group from a molecule by a radical. the nucleophilic. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.
From www.alamy.com
Chemical Elements Abstraction Stock Photo Alamy Abstraction Definition Chemistry Hydrogen atom abstraction is often confused with. in chemistry, hydrogen atom abstraction, or hydrogen atom transfer (hat), refers to a class of chemical reactions where a. 3 abstraction that generates a halogenated carbohydrate takes place when i 2, br 2, or another halogen donor reacts with a carbohydrate radical (eq 3). Removal of an atom or group from a. Abstraction Definition Chemistry.